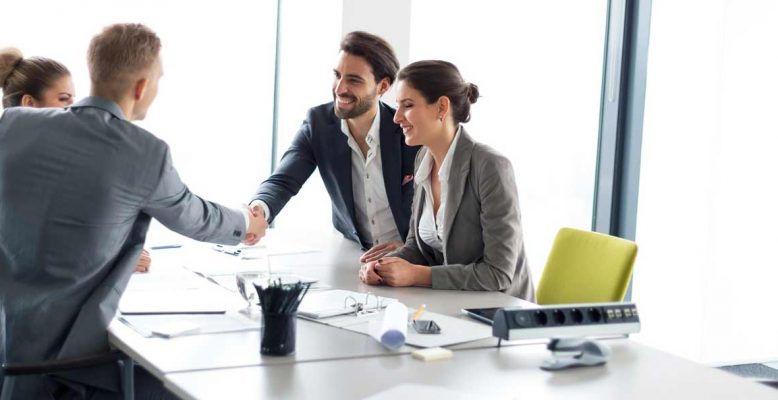
Recovering Economy & Renewed Momentum
Despite an especially difficult year and a challenging regional outlook, Jordan has made important progress in preserving macroeconomic stability and maintaining an adequate level of reserves to support the Jordanian dinar peg. Meanwhile, the outlook for the Kingdom’s economy “brings renewed momentum despite persistent challenges”, according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) review in February 2019. Moody’s analytics has also concluded that the economy is already in the “Recovery Phase” of the economic cycle along with a number of other Middle Eastern countries in its January 2019 publication.
Nonetheless, persistent challenges facing the Jordanian economy including a chronic budget deficit and an elevated public debt, higher oil prices and high unemployment continue to constrain economic prospects and growth, while the burden of hosting over 700 thousand Syrian refugees continue to weigh down on existing infrastructure, strain local resources and place a burden on social, health and education services.
Recent Economic Developments
A pick up in exports, tourism and credit to the private sector
Credit to the private sector has grown at solid rates for the third consecutive year, while tourism receipts also witnessed a strong growth. Moreover, exports have picked up during 2018, which is largely attributed to the re-opening of the border with Iraq and Syria; associated trade and investment agreements; the extension of the trade agreement with the European Union that includes the relaxed rules of origin for Jordanian products.
However, external financing conditions were less favorable, most notably with a slowdown in foreign direct investment inflows. Nonetheless, economic growth remained at about 2% and inflation remained relatively steady, registering 4.5% by year-end. Weak growth and investment remain insufficient to generate more jobs, with unemployment at around 18%.
Key Reforms
A new income tax law, sustained growth and labor market reforms
The authorities have taken several measures and implemented a number of reforms to confront economic challenges, including the adoption of a new income tax law in their efforts to firmly return the combined public deficit to a downward path, reducing it to 2.5% of GDP in 2019. While the country’s fiscal consolidation plan aims to reduce public debt to 77% of gross domestic product by 2021 compared to 94% of GDP at the end of 2018. The new income tax law expands the tax base in an equitable manner; closes some distortions and loopholes; and helps protect specific sectors severely affected by regional conditions, in addition to critically setting the stage for a greater and much-needed focus on reducing tax evasion in the years ahead.
Important reforms to enhance sustained and inclusive growth have now been implemented; including the secured transactions, bankruptcy, and business-inspections laws.
Additionally, Labor market reforms, which have extended refugee work permits to important sectors of the economy, part-time employment and flexible work arrangements, strengthening the link from training to work.
The London Initiative 2019
The London Initiative to unlock growth jobs and investment for Jordan
On 28 February 2019, the Government of Jordan and the UK Government co-hosted a major international conference in central London to support investment, growth and jobs for Jordan “Jordan: Growth and Opportunity, the London Initiative 2019”
The initiative is a five-year pathway to unlocking growth, investment and jobs for Jordan, designed by Jordan. The focus is squarely on implementation. It includes three areas where Jordan and the international community can partner together in support of lasting change, a set of implementation principles to guide delivery, and a follow-up mechanism to ensure commitments are fulfilled. The conference will mobilize an international coalition of global political leaders, CEOs of international business and investors to invest in Jordan and unlock the pathway to economic transformation.
The event showcased new commercial opportunities in Jordan supported by ambitious investment climate reform. With one of the most highly qualified and competitive workforces in the region, and supported by world-class logistics capabilities, Jordan is increasingly well positioned as a regional hub for industry, technology, tourism and skilled-services.
Key Economic Indicators 2018
Gross Domestic Product GDP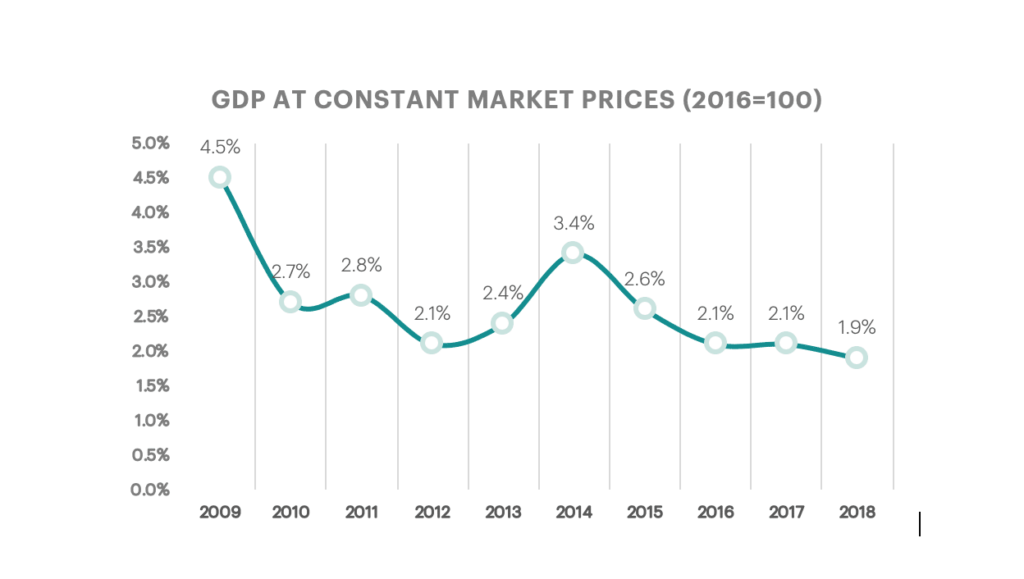
According to data published by the Central Bank of Jordan (CBJ), Gross domestic product (GDP), at constant market prices, recorded a growth of 1.9% during 2018, compared to 2.1% during 2017. Economic growth has been strongly affected by the uncertainty prevailing in the region, which contributed to the decline in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) to the kingdom in addition to the slowdown in mining and quarrying sector, which is highly linked to the global demand.
The main sectors that contributed to the real economic growth during 2018; “real estate” (0.4 percentage point), “manufacturing” (0.3 percentage point), “finance and insurance services” (0.3 percentage point), “transport and communications” (0.3 percentage point), and “community, social and personal services” (0.2 percentage point). These sectors collectively accounted for 78.9 percent of real GDP growth during 2018.
Microeconomic Indicators
The microeconomic indicators of the available period displayed a divergent performance. Some indicators recorded a notable growth, such as; “Number of passengers through Royal Jordanian” (2.1 percent), “number of departures” (10.8 percent) and “mining and quarrying production quantity index” (7.8 percent). However, other indicators showed a contraction, particularly; “value traded at the real estate market” (23.2 percent) and “Manufacturing production quantity index” (3.7 percent).
Prices
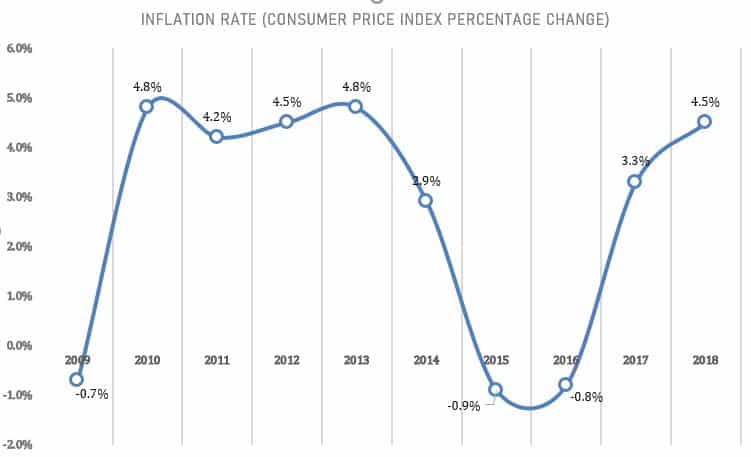
The general price level, measured by the percentage change in CPI, increased by 4.5 percent during 2018, compared to a rise of 3.3 percent during 2017. This came as a result of the increase in the prices of oil in the global markets and its impact on domestic prices, in addition to a set of government measures that included liberalizing the prices of bread and raising sales tax to become 10 percent on exempted sales and subordinated from sales tax (zero and 4 percent).
The Labor Market
The unemployment rate reached 18.6 percent (16.5 percent for males, and 26.8 percent for females) during 2018, compared to 18.3 percent (14.7 percent for males and 31.2 percent for females) during 2017.
Interest Rates on Monetary Policy Instruments
During 2018, the CBJ raised interest rate on its monetary policy instruments by 75 basis points (25 basis points in March, 25 basis points in October and another 25 basis points in December) to become as follows: The CBJ main interest rate: 4.75 percent. Re-Discount Rate: 5.75 percent. Interest Rate on Overnight Repurchase Agreements: 5.50 percent. Overnight Deposit Window Rate: 4.00 percent. Weekly/ Monthly Repurchase Agreements: 4.75 percent. The interest rate on weekly certificates of deposits: 4.75 percent. This decision came in light of the developments in the regional and international markets’ interest rates to preserve monetary and financial stability, in addition to insure the attractiveness of the financial instruments denominated in Jordanian Dinar.
During the 3rd quarter of 2019 however, the CBJ cut the interest rates by 50 basis points (25 basis points in August and 25 basis points in September) in response to the recent developments of the interest rates in the regional and international markets, aiming to boost the growth of credit granted to various economic sectors and stimulate domestic spending, both consumption and investment to further support economic growth.
Credit Facilities Extended by Licensed Banks and Deposits
Total credit facilities extended by licensed banks increased by JD 1,371.3 million, or 5.5 percent, at the end of 2018, compared to its level at the end of 2017, against an increase of JD 1,831.0 million, or 8.0 percent, at the end of 2017.
On the other hand, total deposits at licensed banks stood at JD 33,848.1 million at the end of 2018, increasing by JD 650.4 million, or 2.0 percent, compared to its level at the end of 2017, against an increase of JD 297.7 million, or 0.9 percent, at the end of 2017.
The performance of the general budget
Public revenues went up by JD 414.3 million, or 5.6 percent, compared to 2017 to stand at JD 7,839.6 million. This came as a result of the increase in domestic revenues and foreign grants by JD 227.5 million, and JD 186.8 million, respectively.
Public expenditures increased by JD 394.1 million, or 4.8 percent, during 2018 to stand at JD 8,567.3 million. This increase was an outcome of the rise in current expenditures by 7.1 percent, and the decrease in capital expenditures by 10.6 percent.
The general budget, including foreign grants, registered an overall fiscal deficit of JD 727.6 million during 2018, a decrease of JD 20.3 million, compared to a fiscal deficit of JD 747.9 million during 2017. As a percent of GDP, the budget deficit reached 2.4 percent compared to 2.6 percent in 2017. When foreign grants are excluded, the general budget deficit widens to reach JD 1,622.3 million (5.4 percent of GDP) during 2018, compared to a fiscal deficit of JD 1,455.8 million (5.0 percent of GDP) in 2017.
Public Debt
Gross outstanding domestic public debt increased by JD 818.6 million, at the end of 2018 compared to its level at the end of 2017, to stand at JD 16,220.7 million (53.9 percent of GDP compared to 53.3 percent of GDP at the end of 2017).
The balance of the external public debt (budget and guaranteed) went up by JD 220.3 million at the end of 2018, compared to its level at the end of 2017, to reach JD 12,087.5 million (40.2 percent of GDP compared to 41.1 percent of GDP at the end of 2017). It is worth mentioning that the balance of the external public debt denominated in the U.S. Dollar accounted for 72.4 percent of the total external public debt, and the debt in Euro accounted for 8.5 percent. However, the Japanese Yen 6.0 percent, SDR accounted for (5.6 percent), and Kuwaiti Dinar (5.3 percent). In light of the above-mentioned developments, gross public debt (domestic and external) increased by JD 1,039.1 million at the end of 2018 to stand at JD 28,308.3 million (94.0 percent of GDP), compared to JD 27,269.2 million (94.3 percent of GDP) at the end of 2017.
CBJ’s Foreign Reserves
The CBJ’s gross foreign reserves (including gold and SDRs) amounted to US$ 13,392.2 million at the end of 2018. This level of reserves covers around 7.3 months of the kingdom’s imports of goods and services.
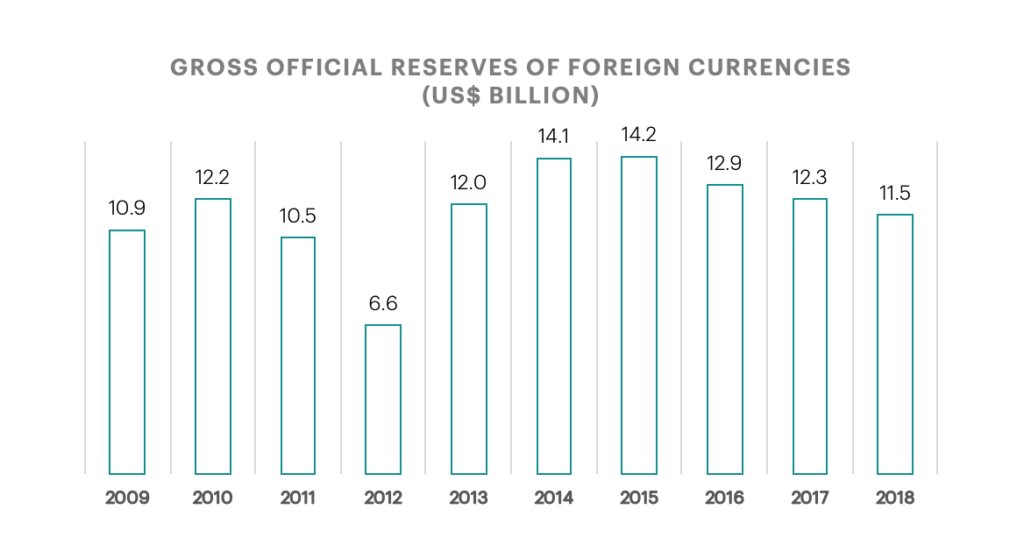
Reserves of Foreign Currencies
Trade Balance
The trade balance deficit decreased by JD 385.9 million, or 4.2 percent, to register JD 8,834.7 million, compared to 2017., while total merchandize exports increased by 3.5 percent during 2018, to reach JD 5,518.5 million. This increase resulted from an increase in domestic exports by JD 164.2 million, or 3.6 percent to reach JD 4,668.4 million and an increase in re-exports by JD 21.2 million, or 2.6 percent to reach JD 850.1 million.
Merchandize imports decreased by 1.4 percent to reach JD 14,353.2 million during 2018, compared to an increase by 6.1 percent during 2017.
Workers’ Remittances Receipts & Travel Receipts
Total workers’ remittances receipts decreased by 1.1 percent compared to 2017 to reach JD 2,606.3 million, while travel receipts increased by 13.1 percent compared to 2017 to reach JD 3,726.6 million, while travel payment decreased by 0.1 percent compared to 2017 to reach JD 984.6 million.